Maturity of polymer processes
Maturity of polymer processes
Race of the technologies
The spectrum of polymer Additive Manufacturing technologies has become wide and continues to evolve. A broad range of different working principles exist, all at different stages of their development cycle. To successfully employ a certain technology, it is important to understand its maturity as well as recent and expected development.
This chapter provides an overview of both established and emerging technology principles and assesses their relative maturity and industrial potential.
What you will find in this section
Polymer AM maturity index
Evaluation with maturity index
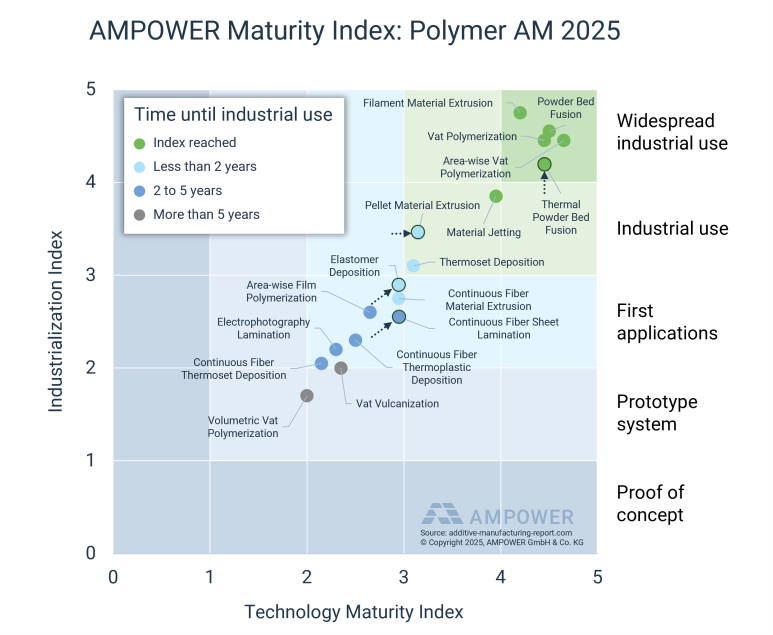
To evaluate the different AM technologies AMPOWER has developed a model to characterize the maturity of an Additive Manufacturing technology based on two indices. The Industrialization Maturity Index and the Technology Maturity Index describe and compare the capabilities and adoption rate of each AM technology in the industrial environment. Both indices are crucial factors for evaluating the current status of any AM technology. Each category is weighted according to its specific importance. Typically, the technological maturity increases first, and the industrialization follows.
Technology Maturity Index
Technology Maturity Index
Industrialization Index
Industrialization Index
Technologies with AM Maturity Index “Prototype system” are still at an early development stage with in-house systems only or on the verge of first systems at beta-customers. Many of the technologies in this corridor are proprietary AM principles or just recently made public.
At a Maturity Index of “First application”, industrial adoption takes place and users introduce the technology in their R&D departments or machines are set up for pre serial production trials at beta-customers.
Technologies at a Maturity Index of “Industrial use” are on the verge of full industrialization. Technologies in this area have not yet been widely adopted as a serial manufacturing technology across multiple industries.
To reach “Widespread industrial use” the technology must be established in multiple industries as a production technology for functional end parts.
Due the industrial focus, AMPOWER does not rate technologies that are still in the proof-of-concept stage.
Established technologies
Powder Bed Fusion, Vat Polymerization and Filament Material Extrusion with widespread industrial use
Several polymer AM technologies, including Powder Bed Fusion, Vat and Area-wise Vat Polymerization, and Filament Material Extrusion, continue to be widely used in industry. These technologies have been utilized by users for over 20 years, resulting in the development of various applications, including end-use parts and tools. In terms of technology, AMPOWER does not anticipate major developments. However, to further industrialize the use of the mentioned technologies, users are demanding significant advancements in the automation of the entire process chain.
As previously mentioned, AMPOWER does not anticipate significant advancements in the established Additive Manufacturing technologies. However, there are some possible advancements in the pipeline.
Some announced developments, such as diode-based or alternative exposure concepts for Powder Bed Fusion, have been discussed for several years but have so far seen limited industrial adoption. If successfully commercialized, such approaches could significantly improve productivity and reduce cost per part. Nevertheless, AMPOWER views this technology as a potential leap forward in increasing productivity and reducing the cost per part, especially if material prices and procurement costs can be lowered.
Further developments in Thermal Powder Bed Fusion have focused on improved part aesthetics, expanded material options, and increased competition among system suppliers. New system architectures and alternative process variants have entered the market, aiming to challenge established solutions and increase adoption in serial production environments.
Electrophotography Sheet Lamination
Technology Maturity Index: Medium
Industrialization Maturity Index: Medium
The status of most technologies has not changed significantly compared to last year. Some especially young technologies have updated their status from a prototype system to the first application category. EVOLVE with their Electrophotography Sheet Lamination technology for example delivered first systems in 2022 to industrial alpha users to test and further improve the system capabilities. AMPOWER expects that this will accelerate the development of the technology and further broaden the polymer Additive Manufacturing possibilities for high volume production. However, the technology is just in the starting phase of its journey towards industrialization and is not expected to reach wide-spread industrial use in the next 5 years. This is caused by the high investment needed and the current lack of experience regarding robustness.
Area-wise Vat Polymerization
Technology Maturity Index: Very High
Industrialization Maturity Index: Very High
Another technological advancement was the introduction of a new approach within the Area-wise Vat Polymerization processes. Two players on the market have presented a similar process, namely CUBICURE with their CERION system and BCN3D with their Viscous Lithography Manufacturing (VLM) technology. These technologies aim to further industrialize the resin market to high volume production. Nevertheless, both are yet to prove their processability and industrial relevance especially when competing with the established vendors.
Volumetric Vat Polymerization
A new entry on the Maturity Index is the Volumetric Vat Polymerization. This technology was introduced by XOLO, a Berlin-based startup. The technology is at the early development stages looking to overcome technical difficulties and develop an industry ready system.
Technology Maturity Index: Low
Industrialization Maturity Index: Low
Thermal Powder Bed Fusion
Technology Maturity Index: Very High
Industrialization Maturity Index: High
In terms of the established technologies no major technological advancements were observed. The status-quo technologies of the industry are still Filament Material Extrusion, Area-wise and Vat Polymerization and Powder Bed Fusion. Further potential for improvement is in the field of Thermal Powder Bed Fusion, where several new market entries will put pressure on HP with its trademarked MJF technology. Increased competition and alternative process implementations are expected to further industrialize Thermal Powder Bed Fusion and close the gap to Laser Powder Bed Fusion for selected applications.
Vat Vulcanization
Technology Maturity Index: Low
Industrialization Maturity Index: Low
The Vat Vulcanization process that was developed by the Swiss startup SPECTROPLAST pushed forward in its development and found suitable applications. The silicone material is of interest for customized consumer goods and medical products with direct skin contact. The latest developments have therefore increased the evaluation of this technology on the AMPOWER Maturity Index. However, also in this case it has yet to prove its capabilities for industrial use cases on a larger scale to step up to “First application” Category.
Pellet Material Extrusion
Technology Maturity Index: High
Industrialization Maturity Index: Medium
Pellet Material Extrusion has not yet made the step into “Industrial use”. However, due to more and more emerging technology suppliers, AMPOWER expects this technology to be further driven towards industrial use quite rapidly. Many users are looking for alternatives to the established Filament Material Extrusion systems due to the high material costs that are often a consequence of the closed material systems. Pellet Material Extrusion is seen as a potential game changer for this market. However, Filament Material Extrusion has a widespread industrial use and established installed base. Hence, new systems of Pellet ME will have to overcome an entry barrier and prove their reliability and feasibility for business cases.
Continuous Fiber Material Extrusion
Technology Maturity Index: High
Industrialization Maturity Index: Medium
With regards to Continuous Fiber Material Extrusion some developments were made. For instance, ANISOPRINT announced an industrial scale system at Formnext 2021. Continuous Fiber Material Extrusion is also available from MARKFORGED and other competitors. However, the reliability of these systems has not yet reached the needs of industrial users. On this basis AMPOWER has not changed the position of this category from “First Applications” to “Industrial Use”.
Material Jetting
Technology Maturity Index: High
Industrialization Maturity Index: High
The established technology of Material Jetting is often forgotten and labeled as a pure prototyping and visual model producing technology. Reason may be that the technology has relatively low competition on the market and that other resin technologies outperform it in terms of throughput. In recent years, several improvements have been introduced that may shift the positioning of Material Jetting beyond pure prototyping applications.