AM Academy
Additive Manufacturing Training
Master Additive Manufacturing with Europe’s Leading Independent Learning Platform
Additive Manufacturing Training Overview
Self-paced online learning programs
and hands-on trainings
Online Learning Programs
Self-paced Additive Manufacturing training programs covering key topics like technology fundamentals, working principles, applications, and market trends. Designed for individuals and companies to learn at their own pace, with regularly updated content to reflect the latest developments in the AM industry.. Go to the Online Learning page.
Workshops and Live Trainings
Hands-on workshops and live Additive Manufacturing trainings combining online courses with expert-led sessions. Whether you’re identifying the right AM parts, improving design skills, or seeking in-depth guidance, our programs deliver practical results. Choose from pre-configured options or customize a course to fit your needs. Go to the live training page.

Selected Customer References




Why AM Academy
Good reasons for the AM Academy
The AMPOWER team behind the Academy combines over 50 years of experience in Additive Manufacturing training as well as over 300 international customer projects and trained more than 500 managers and engineers worldwide. The online learning program is the first of its kind that combines self-made videos with best-in-class content. The focus is on industrial Additive Manufacturing and covers all technologies and industries.
- Broad coverage of all relevant AM technologies
- Self-guided Online Learning Platform and Hands-on Workshops
- Focus on industrial usage and practical tips
- Complete independence and transparency
- Reliable content with regular updates
Discover our online learning programs
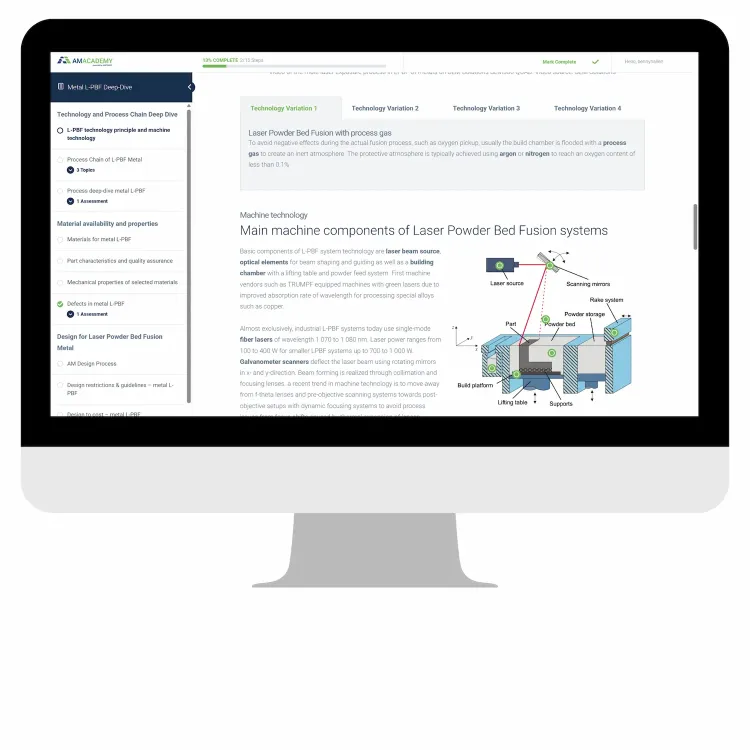
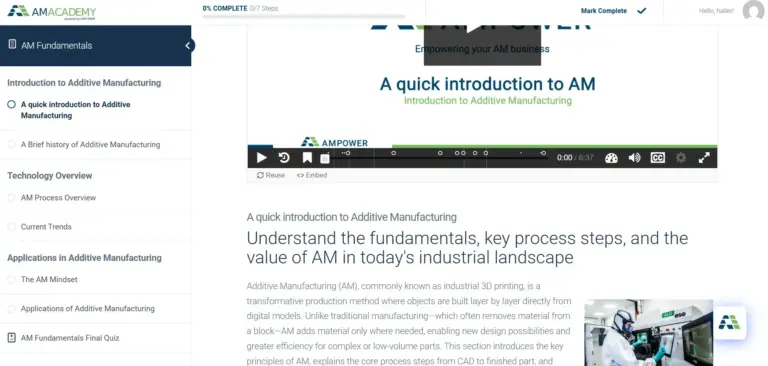
The online learning program consists of several courses covering the most important topics to get started with Additive Manufacturing. Participants can take these courses at their own pace and each course takes about 2-3 hours to complete. The content is explained via illustrations, videos and external content in order to ensure an optimal learning experience. All courses include a wide range of examples from different industries such as automotive, aviation and medical in order to make them easy to understand for every employee. The online learning programs are targeted towards managers, designers and other professionals that are getting started with Additive Manufacturing.
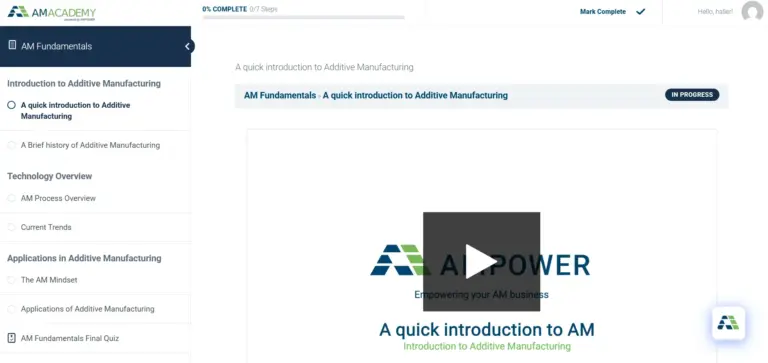



Build up core expertise through live Additive Manufacturing Training
The Additive Manufacturing live trainings are designed to train a small group of people in certain topics. Courses can be assembled based on several theory and practical models to match your requirements. Our team assists you based on experience and pre-defined courses. The hands-on Training on Binder Jetting or metal specialist allow you to experience Additive Manufacturing production.
What our customers say

AM North
Subscribe to start free trial
Fundamentals for free after subscribing to the AMPOWER
Academy newsletter.
Broad coverage of all relevant technologies
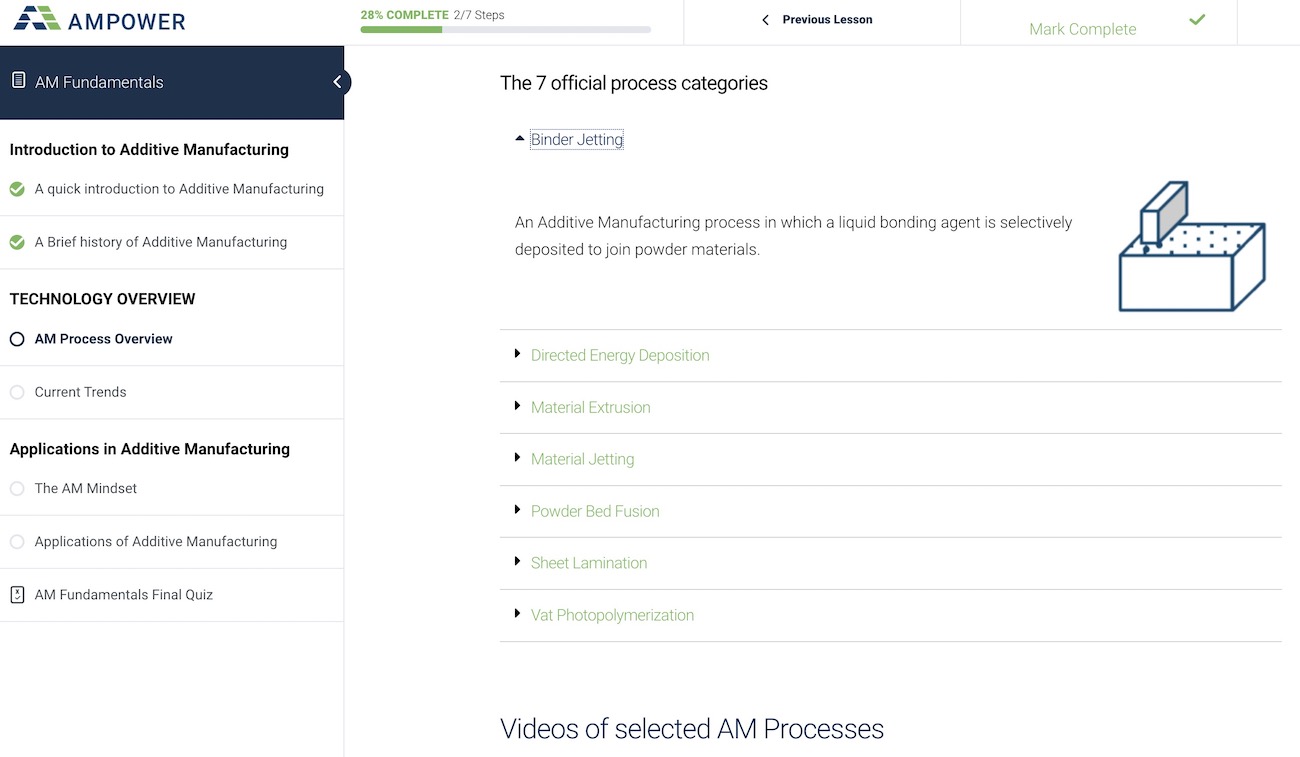
The Additive Manufacturing trainings cover all relevant technologies for metal and polymer Additive Manufacturing. The most mature processes such as Laser Powder Bed Fusion, Directed Energy Deposition or Metal Binder Jetting are covered in more detail to focus on technologies the at are relevant in an industrial context today. For each these technologies, the working principle, typical characteristics and materials are presented together with leading suppliers. Upcoming technologies are constantly evaluated and will be added to the different courses once they have reached a certain maturity in order to ensure that each Additive Manufacturing training stays up to date. The most information about technologies can be found in the courses on Metal Technologies and Polymer Technologies.
Typical applications from different industries
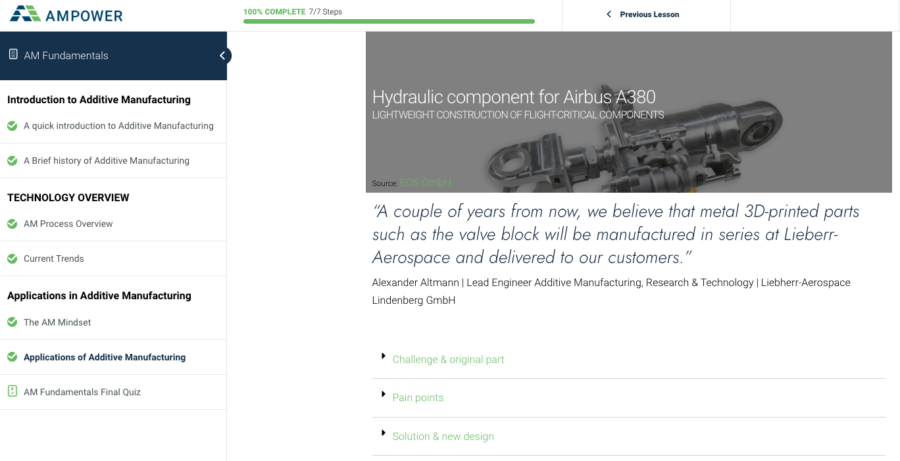
The Additive Manufacturing training programs include a wide range of application examples from different industries such as aviation, automotive and the medical sector. The applications cover the entire value chain including prototyping, tooling, end use components and spare parts. Application examples are presented with background information both on design improvements and the impact on the supply chain of a company. The case studies include background information regarding the technology, materials and companies involved. Applications are used throughout all courses, especially in the courses AM Fundamentals, Metal Technologies and Polymer Technologies.
Actionable advice you can apply to your situation
The Additive Manufacturing training programs contain guidelines that can be applied to your company such as typical characteristics of the most common technologies or the part identification methodology. This ensures that the content that is taught in the online learning programs can directly be applied by the participants in their daily work. Additionally, these methodologies can be applied during the live trainings to create tangible results. The course on Part Identification is best if you would like to apply theoretical knowledge to your business.
What is the basis of the Additive Manufacturing Training programs?
The Additive Manufacturing training programs build on several years of experience in teaching leading industrial companies and professionals. While the initial workshops and trainings were all held in person, over time the trainings have shifted more and more to remote trainings that are delivered online. The current set-up of delivering the most critical skills via self-paced online learning programs and providing in-person trainings to dive deeper and apply the content is seen as the most effective way to create concrete results.

Get Access to our
Additive Manufacturing trainings
as individual users, teams or entire companies.
Get access by selecting one of our plans.