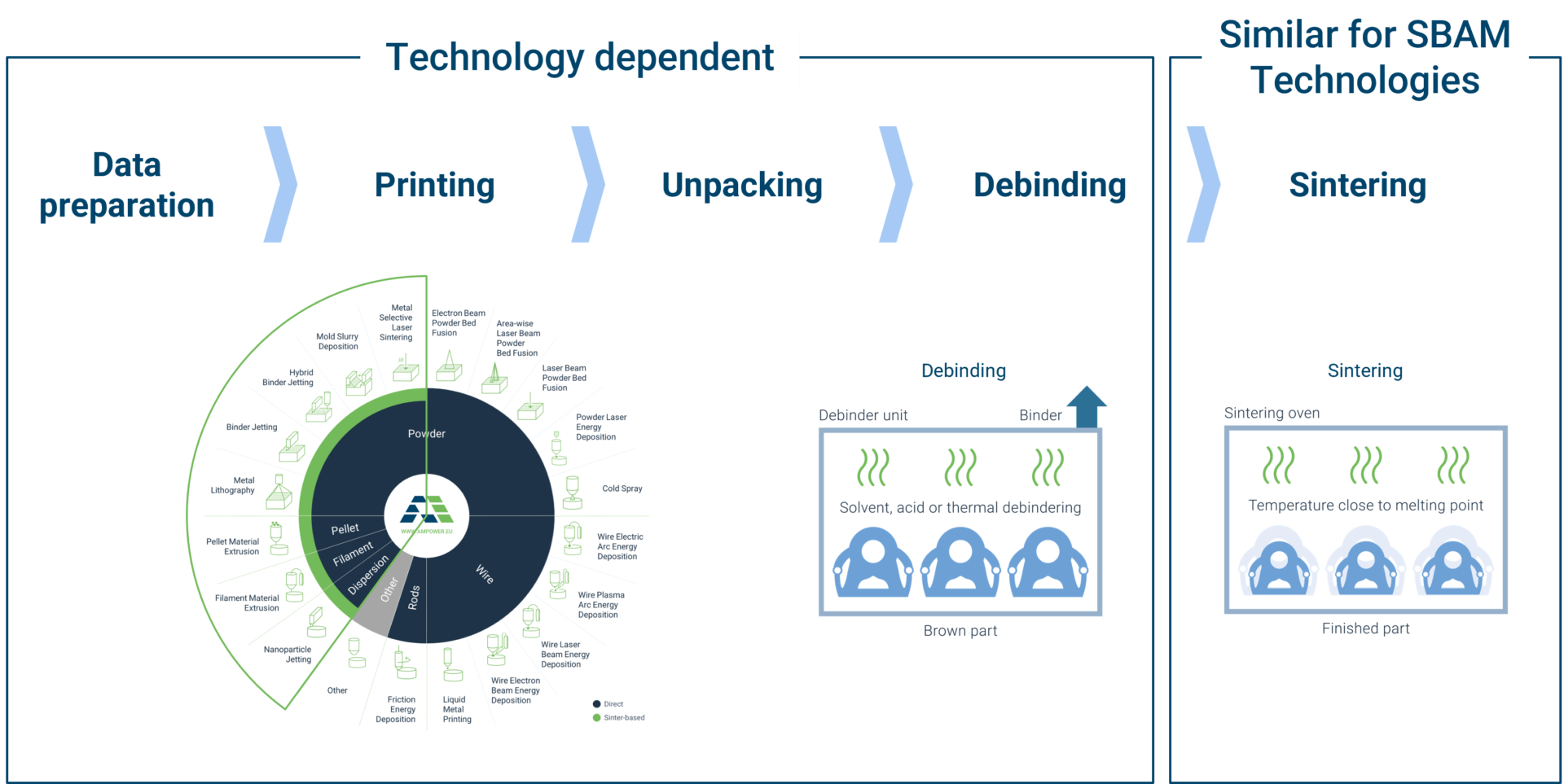
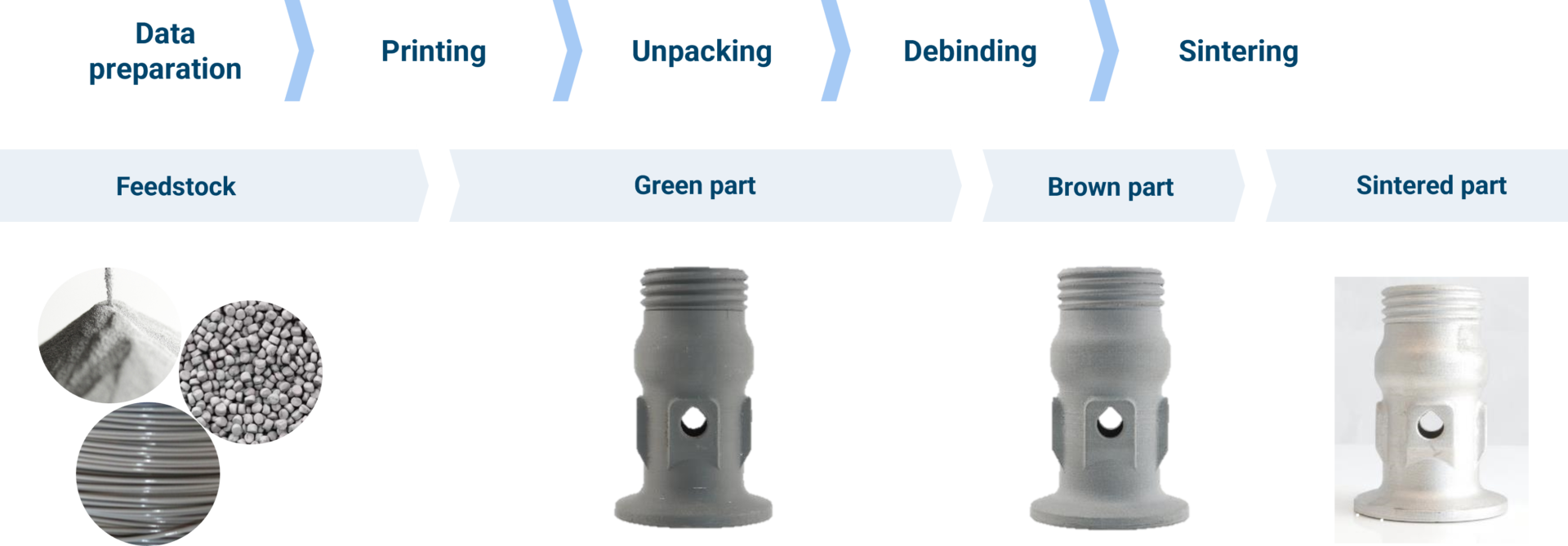
Directed Energy Deposition (DED)
Directed Energy Deposition (DED) includes a range of different technologies with varying feedstock (powder or wire) and energy source (laser, electron beam and arc). DED steadily gained importance, especially within heavy industries due to unique capabilities such as high deposition rates, large component production and the ability to build on existing parts.
In this section, we want to focus on what we consider the two most mature DED processes: Powder Laser Deposition and Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing.
Powder Laser Energy Deposition
Powder Laser Energy Deposition (ED), which is also known as Laser Metal Deposition (LMD), is a welding technology that is known for many years. Recently, more and more AM machine suppliers adopted the technology.
Functional Principle
Powder feedstock is blown through a nozzle onto a meltpool that is formed by a laser on a part surface. This process forms raised welding beads and repeats itself until a three-dimensional structure is created.
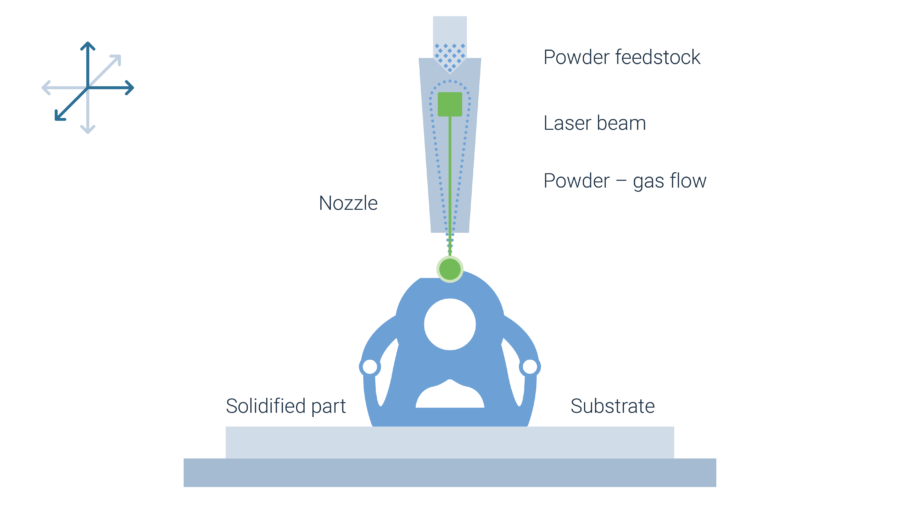
2 different technology variants exist: A processing unit with multi axis system and hybrid systems
Processing unit with multi axis system:
The laser beam and the powder supply are combined in a single processing unit, the working head. In a multi axis system typically the working head as well as the substrate plate on which the part is build are fixed to some kind of motion system. The supplier BEAM uses a gantry with five continuous axes for realization of the processing unit’s motion. TRUMPF offers Powder Laser Deposition systems in which the processing unit head is attached to a robot arm. For rotationally symmetric parts, substrate plates can also be fixed to a rotation-tilt table.
Hybrid Powder Laser Deposition Technology
In a hybrid system, such as from supplier DMG MORI, the Powder Laser Deposition process is combined with a subsequent CNC machining. The build platform is movable around two axes and the process unit head around three axes. After a section of part or the complete part is built, a milling head is extended and finishes the as-printed parts’ surfaces.
A powder feedstock is blown through a nozzle into the process zone, where it is preheated by the laser and then absorbed by the melt pool.
Maturity of Powder Laser Energy Deposition
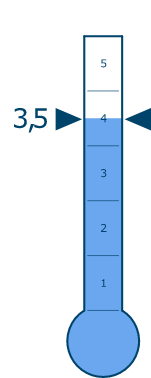
Technology Maturity Index

Powder Laser Energy Deposition display a relatively high technology maturity due to off-the-shelf series machines. However, the technology has not seen significant development during the past few years and is increasingly seeing competition from related technologies such as Wire Laser Deposition.
Industrialization Index
Powder Laser Energy Deposition is used for specific applications such as repair of expensive worn-out parts such as turbine blades. The technology however struggles to identify further viable business cases.
Video of the Powder Laser Energy Deposition process
Below you can see a video of the DED process from Italian machine manufacturer BeAM. They use powder as a feedstock and a laser to melt the powder.

By loading the video, you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Learn more
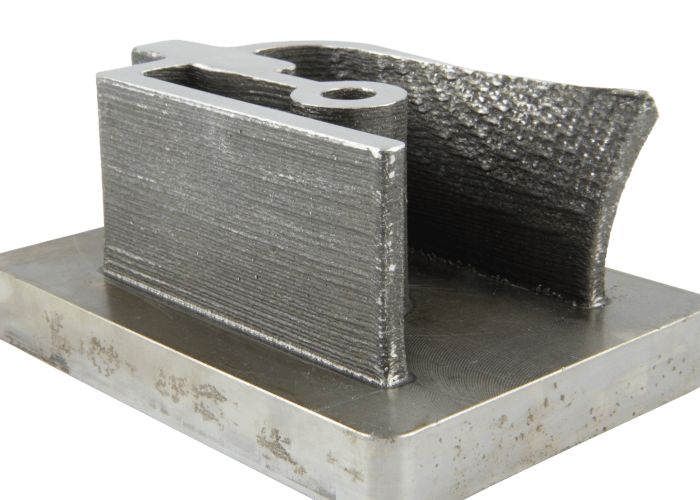
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing
Wire Arc Technologies, also known as Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM), is based on conventional welding processes such as MIG, MAG and TIG welding. The technology has gained lots of attention due to high build speed and low material costs.

Functional Principle
For WAAM, off-the-shelf welding equipment can be used. The wire is fed through a conventional wire-feeding system and is melted by an electric or plasma arc. The motion of the welding torch is provided either by a robotic or gantries system. This way welding beads are placed next to and on top of each other to form a three-dimensional part.
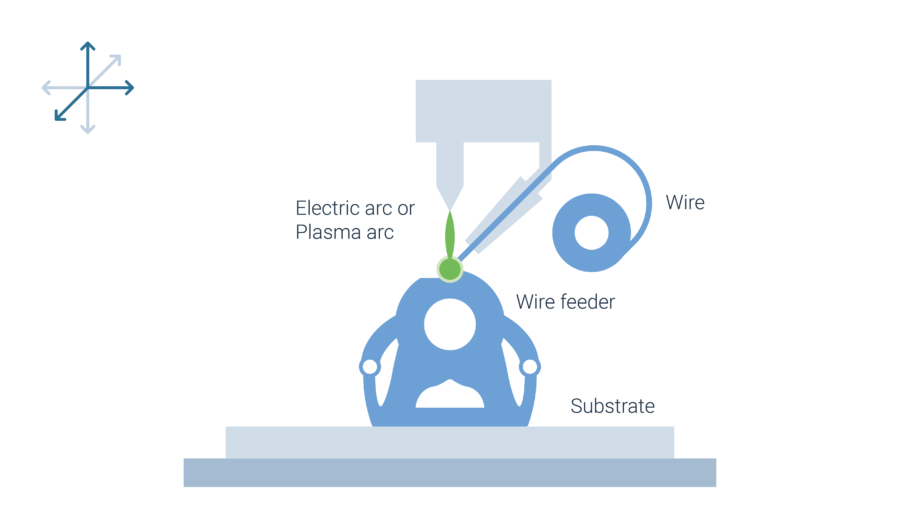
The wire is fed with a conventional wire-feeding system to the working area. The motion of the welding torch can be provided either by a robotic or a gantries system.
For Wire Arc Deposition, existing, off-the-shelf welding equipment can be used. The welding power is provided by an electric or plasma arc that melts the feedstock to create the weld bead.
Maturity of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing
Technology Maturity Index

WAAM machines are generally a combination of off-the-shelf welding torches with an NC handling system. Therefore, the maturity of machine concepts varies greatly from self-made solutions to turn-key solution. The rapidly growing industrialization, however, is expected to further drive maturity of this technology.
Industrialization Index

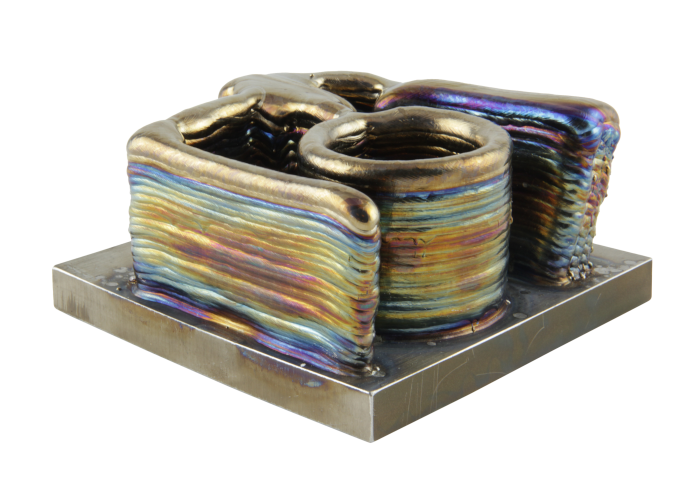
Several niche applications such as fuel tanks in the space industry have further increased the industrial usage of WAAM. One strong driver of the technology is the wide availability of materials since standard welding wired can be used.
Video of the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Process
Below you can see a video of the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing process from German machine supplier GEFERTEC.

By loading the video, you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Learn more
After gaining a brief overview of Directed Energy Deposition, you can dive deeper into process characteristics as well as typical applications of the process by clicking on the topic below.