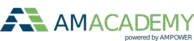Binder Jetting Training
From Theory to Hands-On Expertise with AM Academy & FRAUNHOFER IAPT
Metal Binder Jetting is one of the most promising metal Additive Manufacturing technologies with a high potential for low cost and high-volume digital manufacturing. However, the complete process chain of Binder Jetting is highly complex and the supply chain is still developing. AM Academy created a unique binder jetting training course in cooperation with the FRAUNHOFER IAPT in Hamburg. Participants will learn the theoretical basics accompanied by a comprehensive hands-on session through the complete process chain.
Online learning, theory and practical sessions
Online Learning
Prior to the workshop participants get access to the self-guided online learning course Sinter-based AM Deep-Dive. The content covers basics of sinter-based technologies such as Binder Jetting or Material Extrusion.
Theory Session
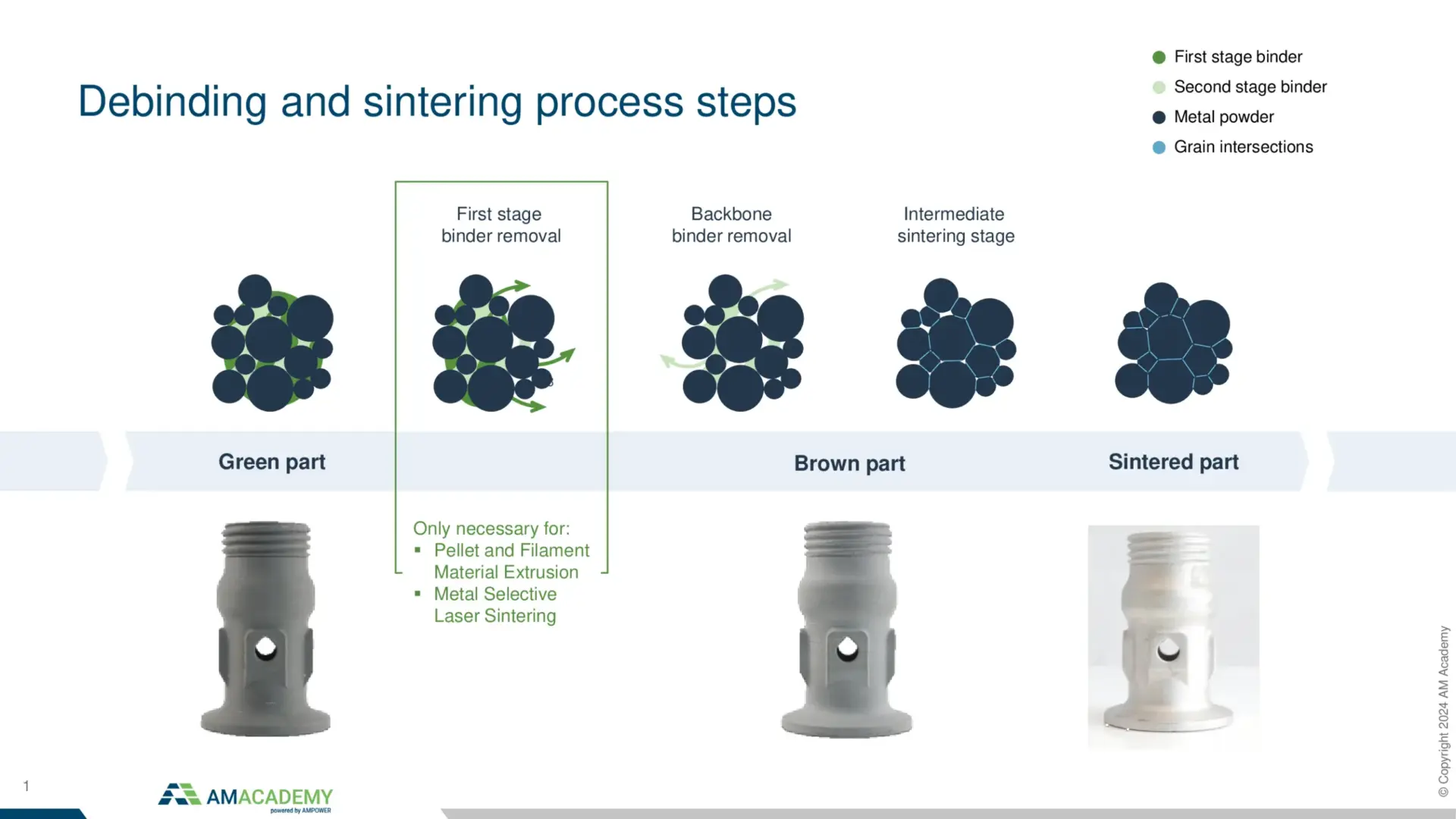
On day one participants will be guided through the theoretical background of the metal Binder Jetting. The program covers a market and technology deep-dive, process parameters and material properties, design rules and as a deep dive into the cost structure. The day will be finalized with a tour through Fraunhofer IAPT’s facilities.
Practical Session
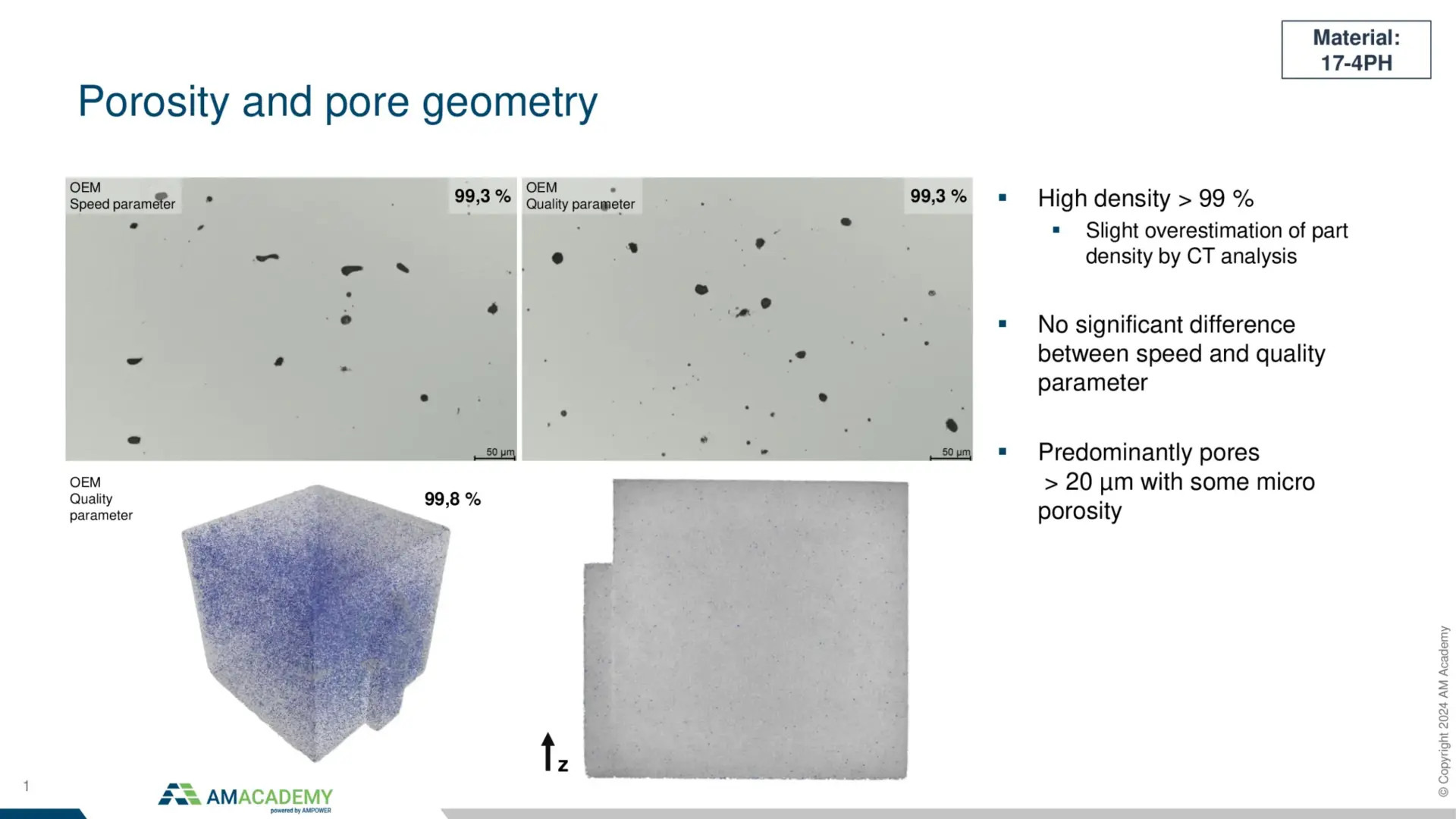
Day two will be the practical hands-on session. Participants will learn about data preparation, parameter settings and machine setup. Next, they will unpack a fully cured build job and prepare the sintering process. At the end of the day, each participant will take home their own Binder Jetting part.
Content Preview
Theoretical Binder Jetting Training
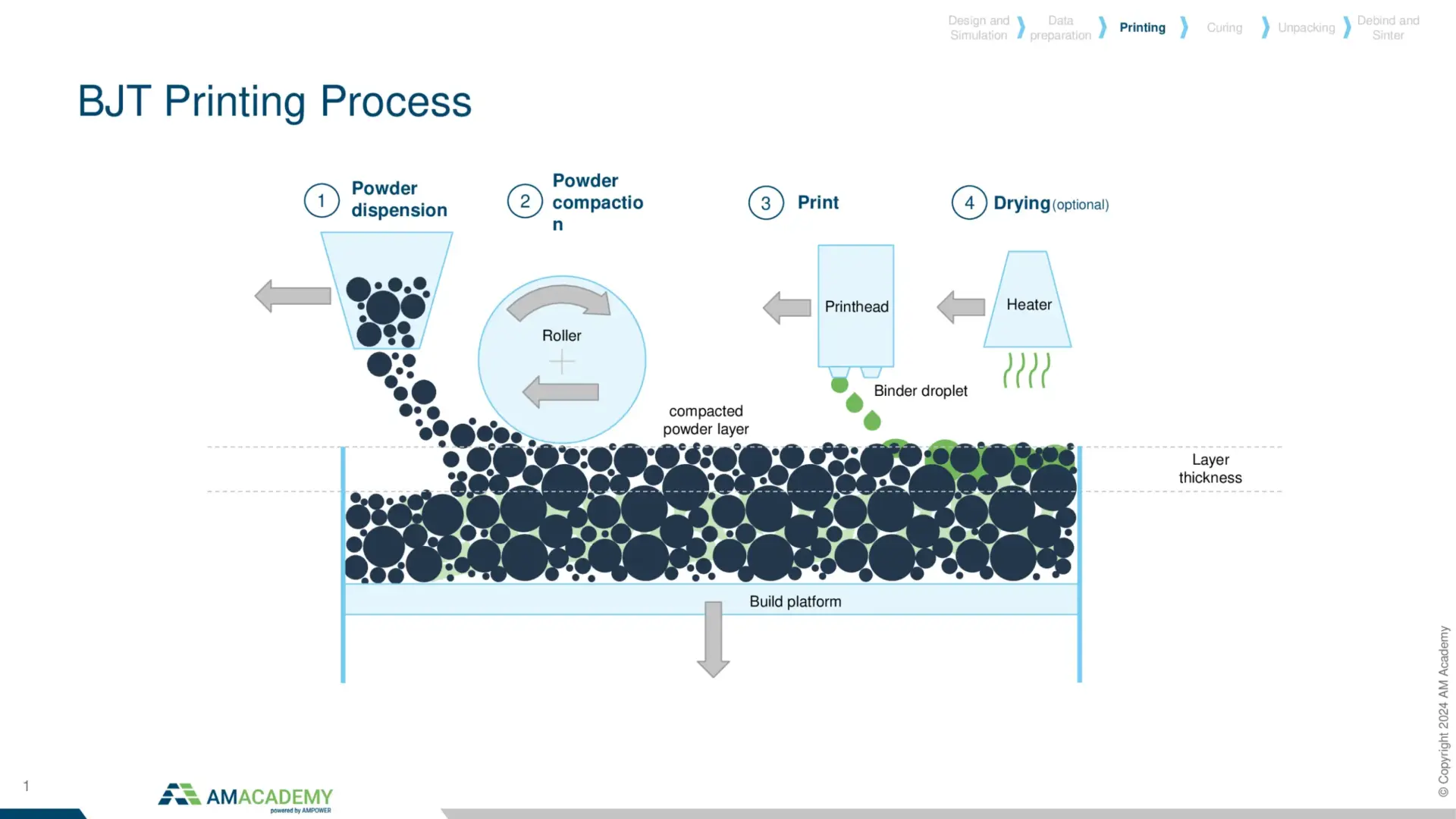
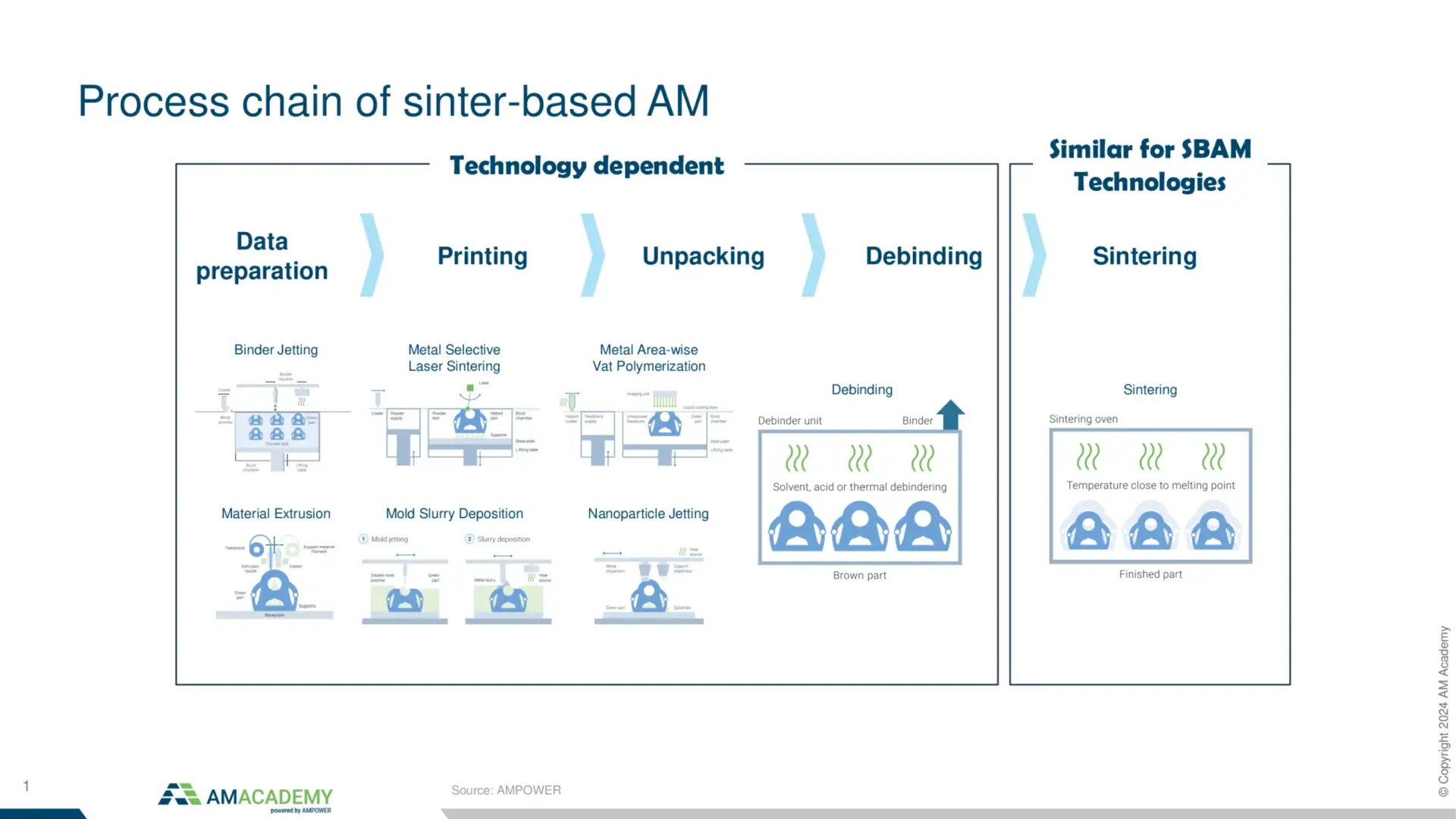
Metal Binder Jetting is a highly complex Additive Manufacturing technology with three major steps of printing, unpacking to sintering. The theory session will begin with a focus on the process parameters and resulting material properties. Based on this knowledge, design limitations and possibilities will be explained. In a practical session, participants will design their very own Binder Jetting component. In the last session of the Binder Jetting training, the cost structure will be covered.
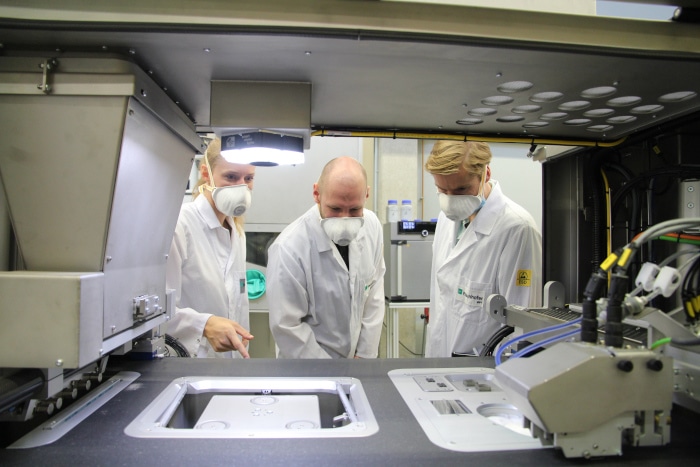

Hands-on Preview
Binder Jetting hand-on training session
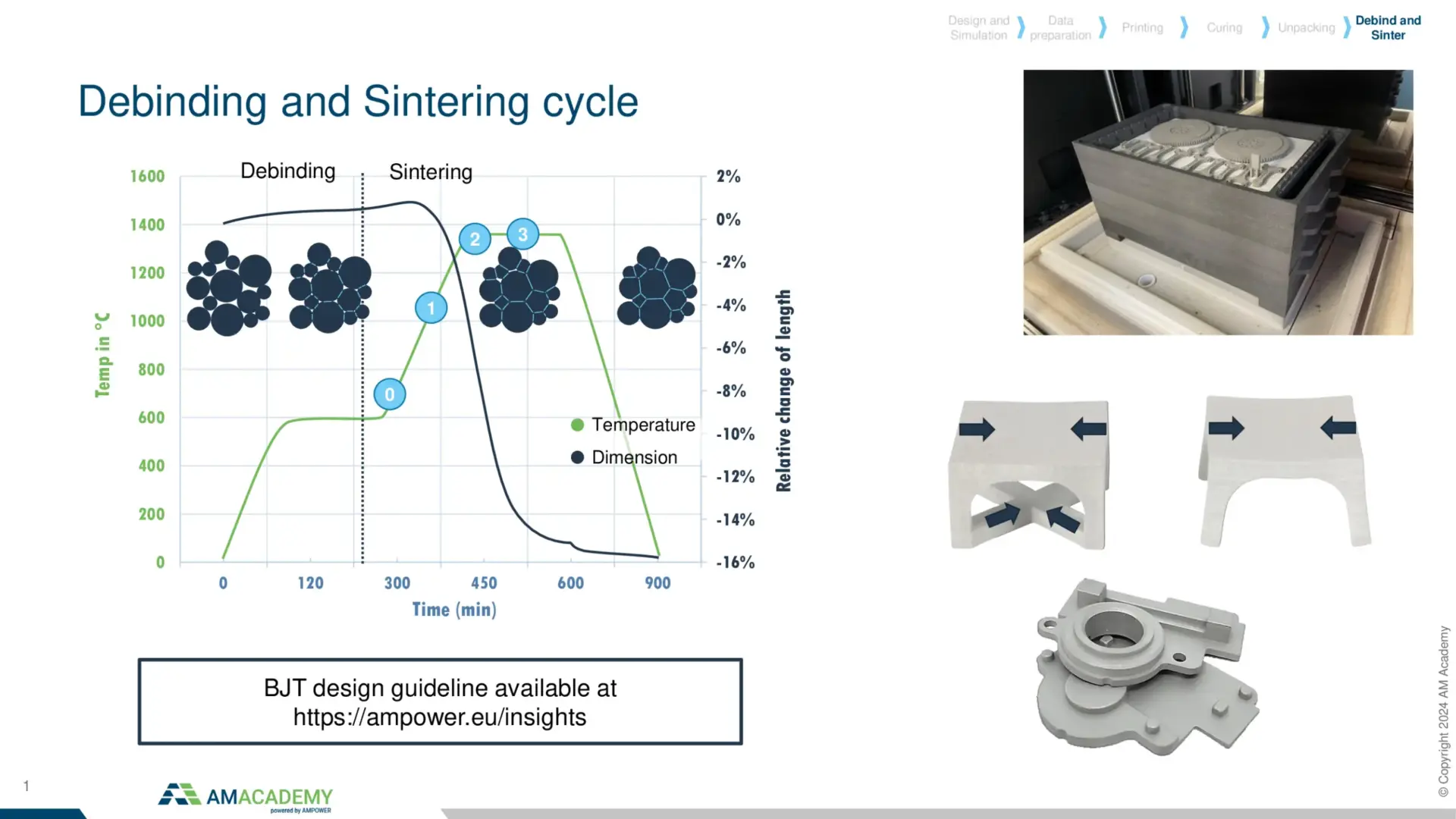
In Binder Jetting there is not only a printing process, but also highly complex depowdering and sintering to be considered. In the joint training of AM Academy and FRAUNHOFER IAPT, participants will learn hands-on how to prepare a machine for printing, how to unpack the green parts from the powder cake and prepare them for sintering. In several design examples, participants will learn about the influencing parameters of the sintering process. After this training, engineers, technicians and managers will have a clear understanding of the potentials and limitations of metal Binder Jetting.
Quick Facts
The first hands-on Binder Jetting training
The AM Academy and FRAUNHOFER IAPT Binder Jetting training is aimed for technicians, engineers and managers with Additive Manufacturing background, who want to understand the potential and limits of Binder Jetting hands-on. Participants will be enabled to make decisions based a training with current state of the art knowledge from an independent source with vast knowledge of the complete Binder Jetting process chain.
- Process chain and parameters
- Feedstock and material properties
- System technology and software
- Design principles
- Cost considerations
- Data and machine preparation
- Unpacking and depowdering
- Sintering preparation
You are looking for a 3D Printing training with industrial production in mind?

Benjamin Haller
Managing Director
Reach out and send a message to our Managing Director responsible for online and live training.