Polymer Material Extrusion
Material Extrusion (ME), often referred to as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), was developed and patented by STRATASYS in the early days of Additive Manufacturing.
After the patent expired in 2009, this technology played a major role in the development of the consumer 3D printing market as well as the expansive adoption of Additive Manufacturing in the industry.
Besides Filament Material Extrusion, more recently several companies have introduced Pellet Material Extrusion machines. Using pellets instead of a filament leads to several advantages such as a higher productivity and lower material cost. In addition, Continuous Fiber Material Extrusion machines can increase the mechanical properties of the produced part.
Technology principle
How does Filament Material Extrusion work?
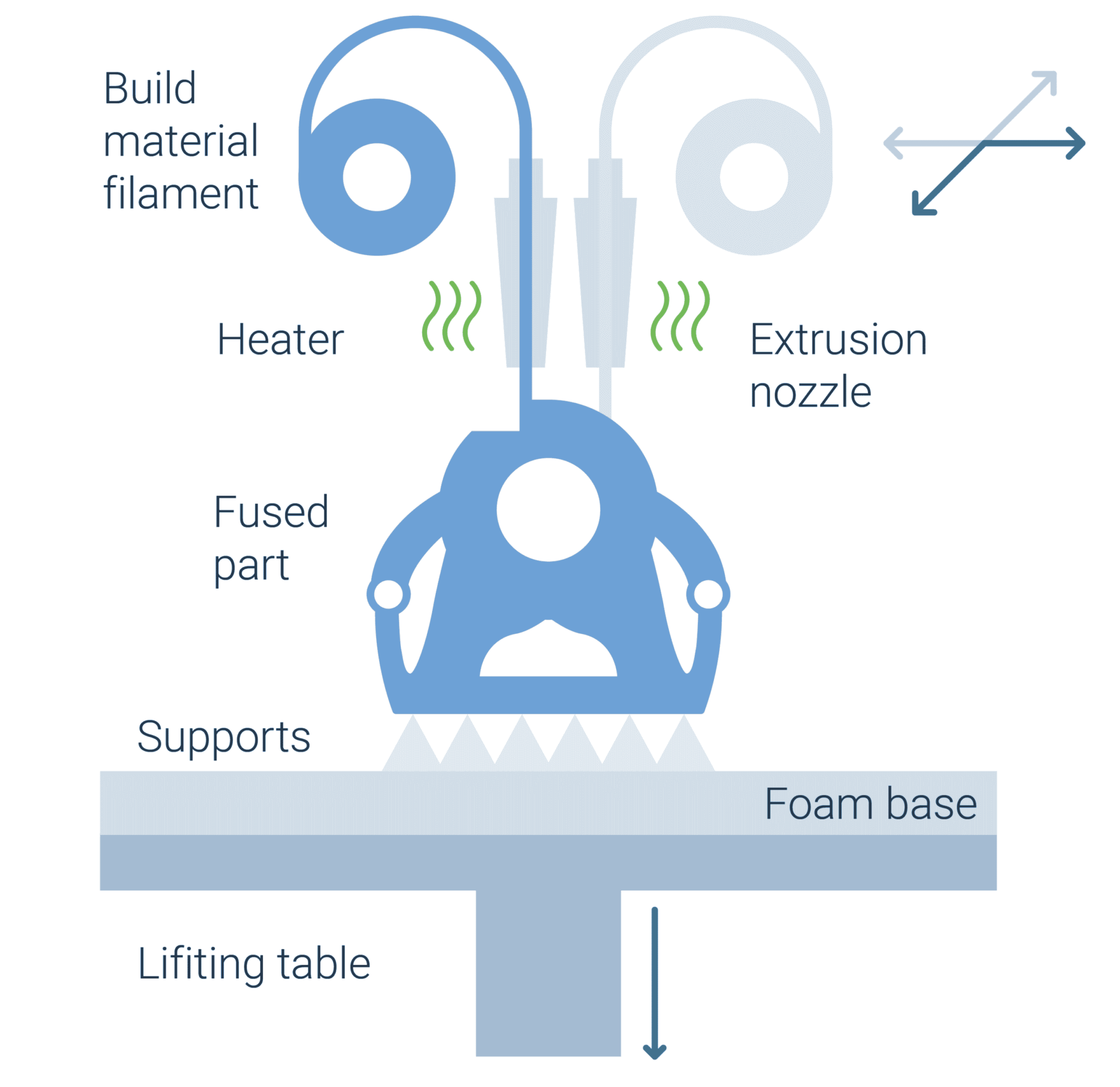
Material Extrusion is based on the extrusion of a thermoplastic feedstock through a heated nozzle. To generate the component the layer is generated by horizontal movement of the nozzle in the x-y-plane. To extrude the next layer, either the nozzle or the base plate is displaced vertically by the desired layer thickness.
Material Extrusion is mainly based on the use of thermoplastic filaments. These filaments are continuously moved through the heater to liquify the filament. The material is then pushed through the extrusion nozzle to create the defined geometry on the build platform. The applied pressure and resulting speed must be steady to achieve good accuracy of the geometry. After the extrusion, the pasty material hardens due to heat conduction into the previously applied layer of the component and forms another solid layer. To some extent multiple materials can be processed to create, for example, soluble support structures or colored components.
The same basic principle of Material Extrusion is used in personal as well as industrial printer. Industrial grade printers often differ from personal printers by the periphery of the build chamber. STRATASYS for example has implemented a heated build chamber to be able to process high performance materials. This feature also used to be protected by a patent.
Read more about this topic in the Polymer Technologies Course.